Contents
What are cervical fibroids?
Cervical fibroids (uterine fibroids) are basically the growth of muscle and tissue on the wall of the uterus.They are not cancerous. Mostly it happens in women, but they are not harmful.Fibroids grow as single nodules or in clusters. They develop into the uterus or outer surface of the uterus.They often appear during years, and they never turn into cancer. Uterus can be distorted from outside and inside if the fibroids get bigger.
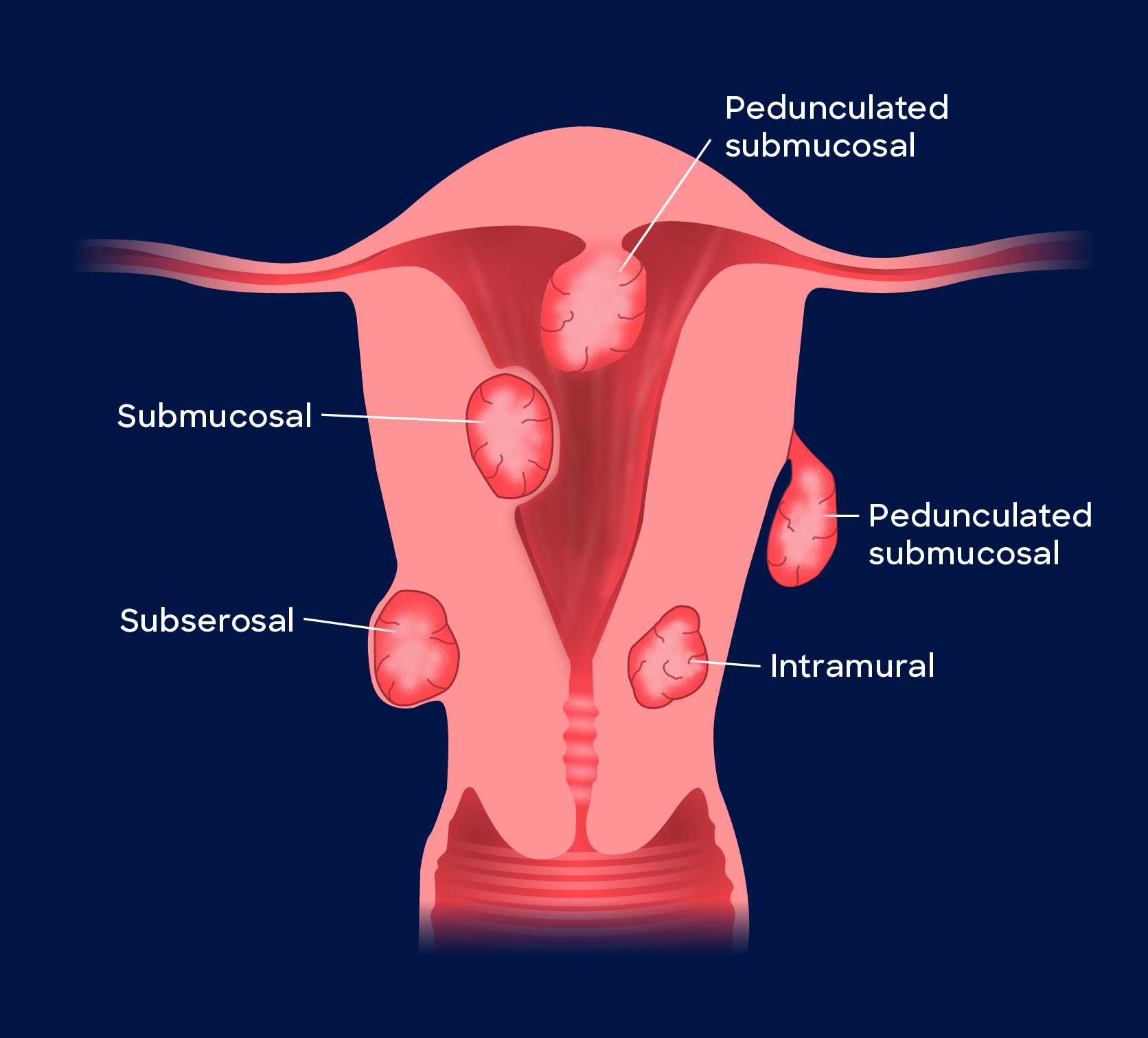
Types of cervical fibroids and their location :
- Intramuscular: embedded into the muscular wall of the uterus.
- Pedunculated fibroids: attached to the uterus and looks kike mushrooms as they are attached with stalk or stem.
- Submucosal fluids: these fibroids grow under the lining of the uterus.
- Subserosal fibroids: this type of fibroids can grow into the uterus.
These fibroids occur mostly between the ages of 30 and 50.
Causes:
- Gene changes: many fibroids contain changes in genes that differ from those in typically uterine muscle cells.
- Hormones: Estrogen and progesterone control the lining of tissues inside the uterus to get thicken with each cycle ,but oversecretion of these hormones can also lead to fibroids.
- Other growth factors: substances that help the body to maintain tissues, such as insulin-like growth factors may affect fibroid growth.
- Extracellular matrix (ECM): This makes cells adhere together like mortar between bricks. It also stores growth factors and can cause biological changes inside the cell .
- The growth patterns of uterine fibroids vary Or they might stay the same size. But some might shrink on their own.
Risk factors for developing Cervical fibroids :
- Race: all people of reproductive age, especially females, could develop fibroids. But black people are more likely to have fibroids because of their racial groups.
- Family history: if your mother or sister has fibroids, you are at a higher risk of getting them.
- Other factors starting before age 10: obesity, low on Vitamin D, having a diet higher in red meat or lower in green vegetables, fruit, and dairy,drinking alcohol,drinking beer—seem to raise the risk of getting fibroids.
- Not having children
- Late age for menopause and obesity
Symptoms of Cervical fibroids :
Most small fibroids don’t cause any symptoms and don’t require treatment other than regular observation by your healthcare provider. Larger fibroids shows symptoms like
- Excessive or painful bleeding during periods.
- Bleeding between your periods.
- Stomach feels full/bloated.
- Frequent urination (this can happen when fibroids put pressure on the bladder)
- Pain in lower area of back
- Constipation
- You are not able to pee.
- Bloating makes you look pregnant.
- Anaemia
Treatment options for cervical fibroids :
Treatment for uterine fibroids can vary depending upon the number and location of fibroids as well as symptoms. Some people even never experience pain. Your treatment might depend upon several factors.
- How many fibroids do you have?
- Size of fibroids
- Where are fibroids located?
- Treatment options include,
Medications:
- Over-the-counter medications help to manage pain and discomfort caused by fibroids.
- Iron supplements: if you have anaemia due to bleeding, you can take iron supplements.
- Birth control: they can also help with symptoms like pills, rings, injections, etc.
- GnRH—gonadotropin-releasing hormones—work by shrinking fibroids.
- Oral therapy: oral therapy is to manage heavy uterine bleeding in people who haven’t experienced menopause with symptomatic uterine fibroids.
Fibroid surgery :
Myomectomy – it is a procedure in which doctors remove fibroids.
There are several types –
- Hysteroscopy: The doctor inserts a thin tool through the vagina into the uterus. Doctor uses the scope to cut and remove fibroids.
- Laparoscopy: provider will use scope to remove fibroids. Here a few incisions will be placed on your abdomen.
- Laparotomy: one larger incision is made into your abdomen, and fibroids are removed.
Complications:
Fibroids don’t interfere with getting pregnant, but some fibroids could cause infertility, and complications include :
- Placental abruption, when an organ brings oxygen and nutrients to the baby, it might separate it from the inner wall of the uterus.
- Foetal growth restrictions : when an unborn baby doesn’t grow as well as expected.
- Preterm delivery is when a baby is born too early, before the 37th week of pregnancy.
Prevention:
You cannot prevent fibroids. But you might lower the risk with changes in lifestyle by :
- trying to stay at a healthy weight.
- Regular exercise.
- In your diet include fruits and vegetables.
- Take birth control pills that might lower the risk of fibroids.
Summary :
Cervical fibroids are the growth of muscle and tissue, and they are generally non-cancerous.Fibroids grow as single nodules or in clusters. They develop into the uterus or outer surface of the uterus. Treatment for uterine fibroids can vary depending upon the number and location of fibroids as well as symptoms. You cannot prevent it, but by taking a few steps, you can reduce the risk of fibroids, like eating good food and doing exercise every day.
References :
- Mayo clinic. Uterine fibroids. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-fibroids/symptoms-causes/syc-20354288
- WebMD. What are uterinefibroids? https://www.webmd.com/women/uterine-fibroids/uterine-fibroids
written by Sabira Athanikar

Pingback: INFERTILITY IN FEMALES - HK Technical PGIMS